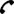Non-destructive Testing
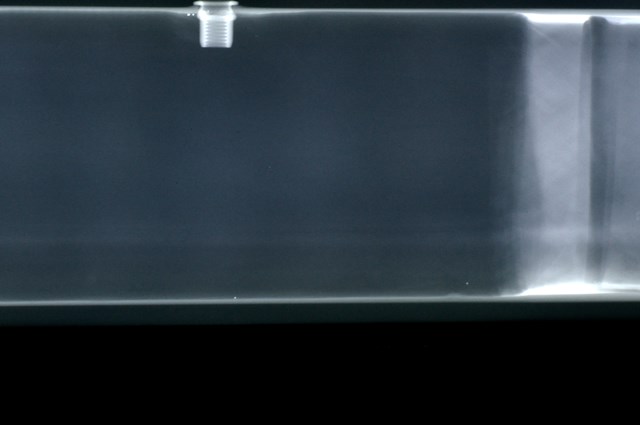
The non-destructive testing (C.N.D.) are the set of examinations, checks and surveys carried out using methods that do not alter the material and do not require the destruction or removal of specimens from the structure under examination. The fundamental characteristic of this type of tests is to be able to analyze a component or measure quantitatively some chemical-physical characteristics of a particular without interfering with the material being tested; they do not modify, even on a microscopic scale, the physical and chemical characteristics and properties of the product in question.
Typical uses of non-destructive techniques are:
- Research and evaluation of defects
- Dimensional checks and checks
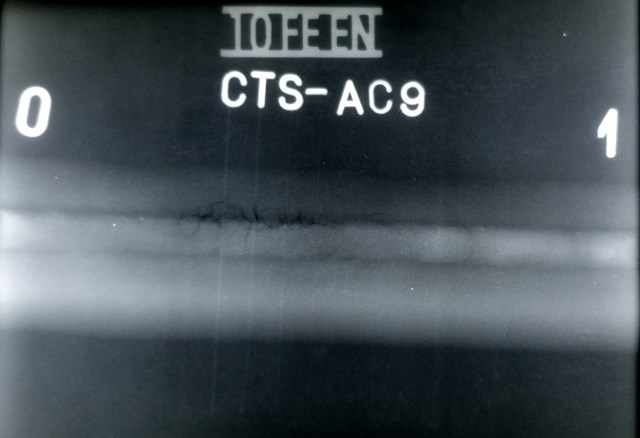
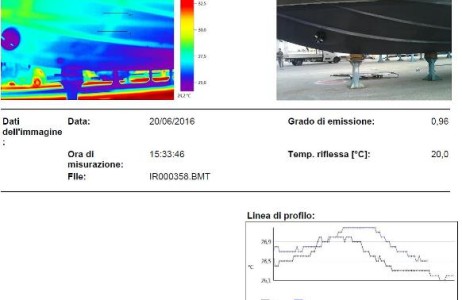
- Thick reliefs
- Deformation measures in static and dynamic conditions
Application fields:
- Research activities – production development
- Checks and checks of material in receipt
- Monitoring, control and improvement of production processes
- Verification of special processes such as: welding activity – heat treatments
- Checking the correct assembly of components and structures before commissioning
- Periodic monitoring and control in service of components, structures and materials critical to the production activity